Identifying Common Birds: A Visual Guide to Avian Diversity


Intro
Identifying common birds can enhance your experience in nature, whether you are a beginner or a seasoned bird watcher. Each bird species brings its own unique characteristics, behaviors, and habitats. This guide aims to provide detailed insights into various common birds found in different environments.
Bird watching is not just about seeing birds; it is about understanding their roles in the ecosystem. Knowledge about their habitats, diets, and behaviors contributes significantly to your appreciation of avian diversity. Through curated images and descriptions, this article invites you to explore the fascinating world of birds.
Understanding Common Birds
Common birds vary widely in appearance, habits, and habitats. Learning to identify them can be a rewarding experience. Here, we provide the fundamentals of avian identification.
- Appearance - Many birds have distinctive colors, sizes, and shapes. Observing these traits can help narrow down the possibilities.
- Habitat - Different species thrive in particular environments such as forests, wetlands, or urban areas. Understanding where a bird lives can aid in identification.
- Behavior - Paying attention to their feeding habits, flight patterns, and calls offers vital clues when trying to identify them.
A keen observer can glean much information about birds beyond their appearance, enhancing your naturalist skills.
Understanding these aspects will not only lead to successful identification but also enrich your experience with nature. Knowing about a bird's role in its habitat fosters a deeper connection to the natural world.
Visual References
Images play a pivotal role in bird identification. They can showcase various species in different stages of life, all enhancing one's understanding of avian diversity. It is beneficial to reference visual guides that highlight:
- Bird silhouettes
- Seasonal plumage changes
- Juvenile versus adult differences
Utilizing high-quality images in tandem with descriptive text will serve as valuable tools for pet owners and bird enthusiasts alike.
Community Insights
Engaging with a community can provide practical tips and shared experiences regarding bird watching.
- User-submitted tips can highlight local species or birding hotspots.
- Real-life encounters expand on published material, adding personal narratives that enrich learning.
- Expert contributions can offer insights on how to observe birds ethically and responsibly.
Leveraging community knowledge helps foster a collaborative approach to bird watching. As you embark on your journey, remember that there is always more to discover about our feathered friends.
Foreword to Common Birds
Birdwatching is an activity that captivates many individuals. Understanding common birds enhances this experience. Recognizing their species allows observers to form connections with the environment. An appreciation for avian diversity can enrich one’s outdoor explorations.
Importance of Bird Identification
Bird identification serves several significant functions. First, it allows individuals to connect with nature on a deeper level. Identifying various species leads to an understanding of their behaviors, song patterns, and migratory habits. This fosters a greater appreciation for the role birds play in our ecosystem.
Furthermore, recognizing bird species can aid in conservation efforts. Understanding which birds are native to a region can inform habitat protection measures. This can directly affect local biodiversity. When people identify and observe birds, they often feel compelled to protect their habitats, especially as urban development continues to encroach upon natural spaces.
Lastly, knowledge of common birds can enhance personal leisure activities. Whether one is photographing, sketching, or simply enjoying a moment in nature, identifying birds can deepen one's engagement with the surroundings. Each interaction becomes more significant, as it comes with learned insights.
The Role of Birds in Ecosystems
Birds play crucial roles in maintaining healthy ecosystems. They contribute to various ecological processes. For instance, many birds are pollinators. When they visit flowers for nectar, they help facilitate reproduction in plants. This, in turn, supports entire food webs.
Furthermore, birds are integral to seed dispersal. Many species consume fruits and nuts, later excreting the seeds away from the parent plant. This promotes biodiversity and helps vegetation thrive in numerous environments. Great-tailed Grackles and Blue Jays are prime examples of this behavior.
Additionally, birds are natural pest controllers. Their feeding habits can keep insect populations in check. This is evident in species like the Purple Martin, which consumes large quantities of flying insects. Such activities contribute to the overall health of agricultural and natural areas.
In summary, observing and identifying common birds is not merely an enjoyable pastime. It is a means to understand the intricate connections within ecosystems. Through this understanding, we can foster appreciation, inspire conservation efforts, and create a more harmonious relationship with nature.
Bird Classification
Understanding bird classification is crucial for anyone interested in the diverse world of avian species. This section elucidates the significance of categorizing birds and provides a foundational insight into avian taxonomy. Proper classification offers clarity when identifying different species and also enhances knowledge regarding their unique characteristics. This information will be particularly valuable for pet owners and bird watchers alike.
An Overview of Bird Taxonomy
Bird taxonomy is the scientific method used to classify living organisms, including birds. It is based on shared characteristics and genetic relationships. Birds are organized into hierarchical categories that include domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. This method helps in understanding the evolutionary relationships between different bird species.
For example, the common house sparrow is categorized as follows:
- Domain: Eukarya
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Aves
- Order: Passeriformes
- Family: Passeridae
- Genus: Passer
- Species: Passer domesticus
Proper taxonomy facilitates bird watchers in making sense of the variety they encounter in their observations. It also supports conservation efforts, as researchers can identify and protect species that may be endangered.
Common Families of Birds
There are several key families of birds that enthusiasts should be aware of. Recognizing these common groups helps in advancing bird identification skills.


Songbirds
Songbirds constitute a large family known for their diverse vocalizations. They are characterized by their melodious songs. Examples include:
- American Robin: Known for its bright orange belly and cheerful song.
- Common Nightingale: Esteemed for its powerful and beautiful singing ability.
- European Blackbird: Recognized for its black plumage and distinct yellow eye-ring.
Waterfowl
Waterfowl are typically found in wetlands and bodies of water. This group includes:
- Canada Goose: Notable for its distinctive honking call and V-shaped flying pattern.
- Wood Duck: Known for its striking colors and unique nesting habits.
- Mallard: A common duck characterized by its green head and engaging quack.
Birds of Prey
Birds of prey are carnivorous and possess keen eyesight. Important members of this group are:
- Bald Eagle: An iconic symbol known for its white head and large size.
- The Peregrine Falcon: Renowned for being the fastest bird on the planet.
- Red-tailed Hawk: Easily identifiable by its red tail and soaring flight.
Woodpeckers
Woodpeckers are captivating due to their unique foraging behavior. This family includes:
- Downy Woodpecker: A small bird with a distinctive black-and-white pattern.
- Red-bellied Woodpecker: Features a striking red cap and a distinctive call.
- Pileated Woodpecker: Recognizable for its large size and prominent crest.
Identifying these common families aids bird watchers in recognizing and appreciating the avian diversity. By understanding these classifications, enthusiasts can enhance their birdwatching experience and foster a greater appreciation for these creatures.
Bird Characteristics
Understanding bird characteristics is crucial for identifying and appreciating common birds. This section focuses on various physical and behavioral traits that can aid both novice and experienced bird watchers. Recognizing these characteristics allows a deeper connection to the avian world and enhances the overall experience of observation and appreciation.
Physical Features of Common Birds
Color Patterns
Color patterns are essential for identification and can vary widely across species. Birds often display distinct colorations that serve multiple purposes including camouflage, mating displays, and territorial behaviors. For instance, the American Robin is easily identified by its orange-red breast against brownish-gray feathers.
The key characteristic of color patterns is their variability, which can signal different roles in avian life. Bright colors may attract mates or scare off rivals while muted tones help in blending into surroundings, providing protection from predators. Understanding these visual cues contributes significantly to identifying birds in their habitats.
One unique feature is seasonal plumage variation. Some birds exhibit different colors during mating season. This can be advantageous for effective communication and competition during breeding periods.
Size Variability
Size variability among birds is another important factor in identification. Birds can vary drastically. For example, the Bald Eagle is a large bird, while the Downy Woodpecker is small and often overlooked. Size often correlates with habitat and behavior, influencing a bird's feeding strategy and nesting preferences.
This characteristic aids in understanding their ecological roles. Larger birds may predate smaller species, while smaller birds often have advantages in reaching narrow spaces for food. The unique feature of size variability becomes relevant when taking note of the context; sometimes size impacts how easily a bird can be observed in given environments.
Beak Shapes
Beak shapes are particularly significant as they are adapted to specific feeding habits. Different shapes can indicate a bird’s diet. For instance, the Wood Duck has a broad, flat bill suited for dabbling or grazing on aquatic vegetation, while the Red-tailed Hawk has a sharp, curved beak ideal for tearing meat.
Understanding beak shapes enriches bird identification efforts and reveals insights into their ecological roles. The unique feature of differing beak structures often signifies how that species interacts with its environment, underlining the intricate balance of ecosystems. Noticing these traits can enhance the experience of birdwatching.
Behavioral Traits
Feeding Habits
Feeding habits demonstrate the adaptability of birds to their environments and available food sources. Different species exhibit diverse strategies. For example, the Canada Goose grazes on grass while the American Robin forages for insects and berries. Observing feeding behavior provides insight into bird behavior and preferences.
The key characteristic of feeding habits is their reflection of ecosystem health. Species that thrive indicate healthy environments, while declines may signal issues in local ecosystems. Unique feeding techniques, such as the Peregrine Falcon's high-speed stoop, underscore the varied approaches birds use to secure food. This information can be useful for aspiring bird watchers in understanding local species.
Mating Rituals
Mating rituals among birds are fascinating and often elaborate, serving both as a mechanism for reproduction and as a means of establishing territory. Many species engage in displays such as song, dance, or colorful plumage during mating seasons. The Common Nightingale, for example, is known for its beautiful song which attracts partners.
Key characteristics include the diversity of courtship behaviors, reflecting different ecological niches and survival strategies. Recognizing these behaviors contributes to a deeper understanding of avian life cycles. One unique aspect is the role of male displays, which often influences female choice and reproductive success. Observing these rituals can be particularly rewarding for bird enthusiasts.
Nesting Preferences
Nesting preferences signal key information about a bird's survival strategies and habitat selection. Many species prefer specific nesting environments, such as tree cavities, open fields, or wetlands. For example, the Red-bellied Woodpecker frequently nests in tree hollows, while others like the Mallard might nest on the ground near water.
The key characteristic of nesting preferences lies in their correlation with survival. Birds select nesting sites based on safety from predators and accessibility to food. Unique nesting strategies, such as the elaborate nests built by European Blackbirds, can indicate adaptability to changing environments. Understanding these preferences allows bird watchers to predict where to observe specific species.
List of Common Birds with Pictures

Understanding the diversity of common birds is crucial for both novice enthusiasts and seasoned bird watchers. This section aims to provide valuable insights into a spectrum of birds that inhabit various regions. Here, a visual reference accompanies each bird discussed, enriching the reader’s connection to these avian species. By categorizing birds into distinct groups, this guide makes identification easier and more intuitive.
Songbirds
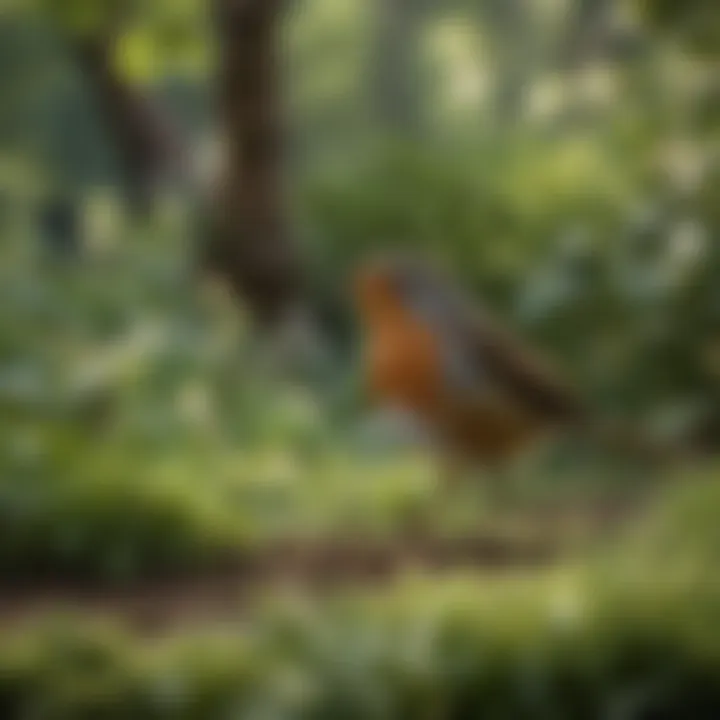
American Robin
The American Robin is a well-known bird, often recognized by its vibrant orange breast and cheerful song. This species plays a significant role in the ecosystem as a seed disperser. The robin is a popular subject for birdwatchers, thanks to its approachable demeanor and striking appearance. One distinct feature of the American Robin is its melodious call, which is often heard during early spring. Its adaptability to urban settings makes it easily observable in many areas, providing birdwatchers a rewarding experience.
Common Nightingale
The Common Nightingale, famous for its beautiful and complex song, adds a unique flair to the birdwatching experience. This species often captivates listeners in wooded areas, especially during the breeding season. The nightingale’s main characteristic is its vocal range, which is regarded as one of the finest in the avian world. An interesting feature is its nocturnal singing habits, making it a delightful companion during nighttime walks. Observing the nightingale requires patience, as it can be elusive during the day.
European Blackbird
The European Blackbird is a distinctive bird, easily recognizable by its glossy black plumage and bright yellow eye-ring. This species contributes to the garden ecosystem, often being seen foraging on the ground for insects and berries. Its characteristic song is rich and varied, marking its presence in both rural and urban settings. The blackbird’s adaptability to various environments enhances its appeal among bird watchers. However, its cautious nature means it sometimes shies away from human presence.
Waterfowl
Canada Goose
The Canada Goose is a well-adapted waterfowl known for its distinctive honking and V-shaped flying formation. This bird plays a vital role in wetland ecosystems, acting as a grazier that helps shape plant communities. A key characteristic is its long neck and distinctive black head with a white chinstrap. It is a frequent sight in parks and lakes, making it a familiar bird for many people. However, Canada Geese can be aggressive, particularly during nesting season, which necessitates caution when observing them in close proximity.
Wood Duck
The Wood Duck is one of the most aesthetically striking waterfowl, recognized for its iridescent plumage and intricate patterns. It often inhabits wooded ponds and lakes, favoring areas with dense vegetation. A unique aspect of the Wood Duck is its ability to perch on branches, unlike many other waterfowl species. Its beauty makes it a sought-after subject for photographs and observations. However, its preference for secluded habitats might make sightings rare for some bird watchers.
Mallard
The Mallard is perhaps the most recognized duck species worldwide, noted for its distinctive coloration and adaptability. The males boast a vibrant green head, while females are mottled brown. Mallards play an important role in aquatic ecosystems and are often seen in parks or near water sources. Their friendly behavior toward humans makes them a favorite among bird watchers. However, they can be prone to crowding in popular areas, which may limit a more serene bird watching experience.
Birds of Prey
Bald Eagle
The Bald Eagle stands as a symbol of freedom and strength, making it an iconic species among bird watchers. This bird of prey plays a pivotal role in maintaining the health of ecosystems as a top predator. One of its key characteristics is the impressive wingspan and striking white head, easily recognizable across vast landscapes. Observing a Bald Eagle in flight is a breathtaking experience, however, they inhabit particular regions that might require specific locations for spotting.
The Peregrine Falcon
The Peregrine Falcon is renowned for being the fastest bird in the world, diving at incredible speeds to catch its prey. Its contribution lies in controlling populations of small birds, thereby maintaining balance in the ecosystem. The falcon’s characteristic bluish-gray plumage and yellow facial markings make it a beautiful sight. However, its high-speed flights and preference for urban areas might challenge birdwatchers trying to observe its hunting techniques.
Red-tailed Hawk
The Red-tailed Hawk is commonly seen soaring across various terrains, showcasing a strong presence in North America. This bird of prey contributes significantly to rodent population control, reflecting the natural balance of ecosystems. One defining feature is its reddish-brown tail, visible during flight. Observers appreciate its adaptability to different habitats, but patience is essential, as their preferred soaring heights might make them less observable at times.
Woodpeckers
Downy Woodpecker
The Downy Woodpecker is a small but intriguing bird characterized by its black-and-white plumage and short bill. This woodpecker plays an important role in controlling insect populations and nourishing trees. One unique feature is its habit of tapping on tree bark, often seeking out insects hidden in the wood. Bird watchers find this species accessible, often spotting them in both rural and urban settings. However, its small size can make it difficult to see amongst the foliage.
Red-bellied Woodpecker
The Red-bellied Woodpecker is notable for its striking appearance and drumming sound. This bird contributes to tree health through its foraging techniques to find insects. Its red cap is a distinctive feature, although the red belly might be understated. Bird watchers often enjoy tracking this species due to its adaptability to various environments. However, like the Downy Woodpecker, it might blend into its surroundings, making it a challenge to spot at times.
Pileated Woodpecker
The Pileated Woodpecker is a large and striking bird, known for its loud calls and impressive size. This species contributes to forest ecosystems through its excavation of tree bark, aiding in the decay process. Its characteristic red crest and bold markings make it a standout among woodpeckers. While its size allows for easier spotting, its preference for dense forests can make opportunities for sightings limited. Observing a Pileated Woodpecker in its natural habitat is rewarding but requires some effort.
Bird Habitats
Bird habitats play a crucial role in understanding avian behavior and biodiversity. Recognizing the different environments where birds thrive contributes significantly to effective birdwatching and conservation efforts. Each habitat type hosts unique bird species, promoting a diverse range of characteristics and behaviors.
Common Bird Habitats Explained
Forests
Forests are vital environments for many bird species. Their dense canopy provides shelter, food sources, and breeding grounds. The key characteristic of forests is their vertical structure, which includes layers like the canopy, understory, and forest floor. This stratification allows various bird species to exploit different niches, making forests a popular choice for birdwatching enthusiasts.
A unique feature of forests is the presence of specialized feeding areas. For example, various songbirds forage for insects under leaves or among branches. The advantages of forests include support for high biodiversity. However, deforestation poses significant threats, leading to habitat loss.
Wetlands
Wetlands are important ecosystems that support numerous bird species. They serve as critical locations for feeding, breeding, and migration. Wetlands' key characteristic is the accumulation of water, which creates a rich habitat for fish, insects, and plants, attracting bird populations.


This habitat is favorable for birdwatching because it provides opportunities to observe both resident and migratory species. A unique feature of wetlands is their seasonal variability; changing water levels can influence bird feeding behaviors. However, wetlands are susceptible to pollution and habitat destruction, which impacts their ecological balance.
Urban Areas
Urban areas may seem less hospitable for birds, yet they offer unique opportunities for birdwatching. The essence of urban habitats lies in human-altered landscapes that can still support diverse avian life. The key characteristic of urban areas is their mix of green spaces, such as parks and gardens, alongside built structures.
These features can provide crucial resources like nesting sites and food. A unique aspect of urban areas is how adaptable some bird species are to these environments. For instance, pigeons and sparrows thrive in city settings. However, the challenges of urban habitats include limited natural resources and increased danger from predators and vehicles.
Recognizing the importance of different bird habitats can enhance birdwatching experiences and contribute to effective conservation efforts.
In summary, understanding the specific aspects of forests, wetlands, and urban areas enriches the knowledge of bird habitats. Observers can adapt their strategies and appreciate the avian diversity present in these unique environments.
Bird Watching Tips
Bird watching is not just an enjoyable pastime but also a valuable tool for understanding our natural world. It connects individuals to the environment and helps cultivate an appreciation for avian species. Engaging with this activity requires knowledge about what to observe, the tools to use, and methods to increase your chances of successful sightings.
Equipment for Bird Watching
Binoculars
Binoculars are perhaps the most vital tool for any bird watcher. A good pair enhances the viewing experience significantly. Their key feature is magnification, which allows watchers to see details from a distance that would otherwise be invisible.
A popular choice is the Nikon Prostaff 3S. The Nikon Prostaff offers a magnification of 8x42 which provides a clear and bright image. Its lightweight design and non-slip grip make it easy to handle. However, it’s essential to note the trade-off between size and portability. Larger binoculars may provide better optics but can become cumbersome during long observation periods.
Cameras
Cameras are increasingly becoming important in the bird-watching community. They allow enthusiasts to capture images of the birds they observe. A key characteristic is the type of lens used. A camera with a good zoom capability—like the Canon EOS 90D—is beneficial for bird photography.
The Canon EOS 90D has a 32.5 Megapixel APS-C sensor, which is excellent for high-resolution images. It also allows rapid shooting, which is useful when capturing fast-moving subjects. The downside can be the cost and the learning curve involved to use more advanced features effectively.
Field Guides
Field guides are crucial for bird watchers of all levels. They provide detailed descriptions and visual references that help in identifying species. A key characteristic of these guides is the level of detail concerning local birds. Guides like
Conservation and Protection
Conservation and protection of birds is an essential topic within the sphere of avian study. Birds contribute significantly to our ecosystems by aiding in pollination and seed dispersion. They serve as essential indicators of environmental health. The decline in bird populations can signal deeper ecological issues, making their conservation crucial. Every individual bird species plays a role in maintaining the balance of nature, and their decline can lead to unforeseen consequences.
The Role of Bird Conservation
Bird conservation focuses on preserving bird species and their habitats. It addresses threats like habitat loss, climate change, hunting, and disease. The establishment of protected areas, such as national parks and wildlife refuges, plays a vital role in conserving both species and their ecosystems. Often, efforts also involve research and monitoring of bird populations to understand their needs better.
Conservation initiatives also promote public education. Raising awareness about the importance of birds can mobilize communities to participate in protection efforts. Programs that engage local populations in conservation efforts help secure a future where bird species can thrive.
Benefits of Conservation
- Ecosystem Services: Birds offer many ecosystem services, including pest control and pollination.
- Biodiversity: Maintaining bird populations contributes to overall biodiversity, which is essential for ecosystem stability.
- Cultural Significance: Birds also hold cultural significance; they inspire art, music, and literature.
Conserving birds helps sustain the intricate web of life that connects all organisms.
How to Contribute to Bird Conservation
Bird conservation is a collective effort that requires participation from everyone. Here are some ways to contribute:
- Support Local Organizations: Many local organizations work hard to protect bird habitats. Supporting them can amplify their impact.
- Participate in Citizen Science: Engage in programs like the Audubon Society's Christmas Bird Count. This helps scientists collect important data on bird populations.
- Create Bird-Friendly Spaces: In gardens and yards, native plants can provide food and shelter for local birds. Avoiding pesticides also helps maintain healthier environments.
- Advocate for Conservation Policies: Supporting legislation designed to protect avian habitats is vital.
- Educate Others: Share knowledge about bird conservation with friends and family to raise awareness.
By taking these actions, individuals can make significant contributions to bird conservation efforts. Every action counts. The future of these species is in our hands.
Finale
In the journey of understanding common birds, the conclusion serves several key purposes. First, it recaps the valuable insights gathered throughout the article, highlighting bird species, habitats, and their characteristics. This synthesis reinforces the knowledge that readers have acquired, making it easier to recall important details in future birdwatching activities.
Moreover, this concluding section emphasizes the significance of bird identification and conservation. Recognizing various species not only enriches the birdwatching experience but also fosters a deeper connection with nature. Understanding the role of birds in ecosystems contributes to more informed decisions about conservation efforts. As stewards of our environment, being aware of avian diversity can motivate individuals to participate in protective measures that benefit these species.
Lastly, this conclusion encourages continued engagement with the avian world. It invites readers to apply their newfound knowledge in practical settings, whether through casual observing or committed conservation activities. Overall, the conclusion encapsulates an appreciation for birds while guiding readers towards further exploration and action.
Recap of Key Points
- Importance of Bird Identification: Understanding different species enhances enjoyment and fosters a connection with nature.
- Diversity of Habitats: Birds inhabit various environments, each contributing to their unique behaviors and characteristics.
- Conservation Efforts: Knowledge gained can support actions that protect bird populations and their habitats.
This recap serves as a reminder of the critical themes in bird identification.
Encouragement for Future Engagement
To foster a lasting interest in the world of birds, readers are encouraged to stay curious. Consider participating in local birdwatching clubs or following bird identification resources online. Engaging in conversations with fellow enthusiasts on platforms like Reddit can expand your understanding and appreciation of avian life.
Moreover, try to implement what you've learned. Take notes during observations, or begin a sketchbook of the birds you encounter. These activities can deepen your engagement and enhance your skills as a birdwatcher.
Birds are all around us, and every sighting can be a learning moment. Keep exploring and discovering, as each new experience enriches your connection with the avian world.







